728x90
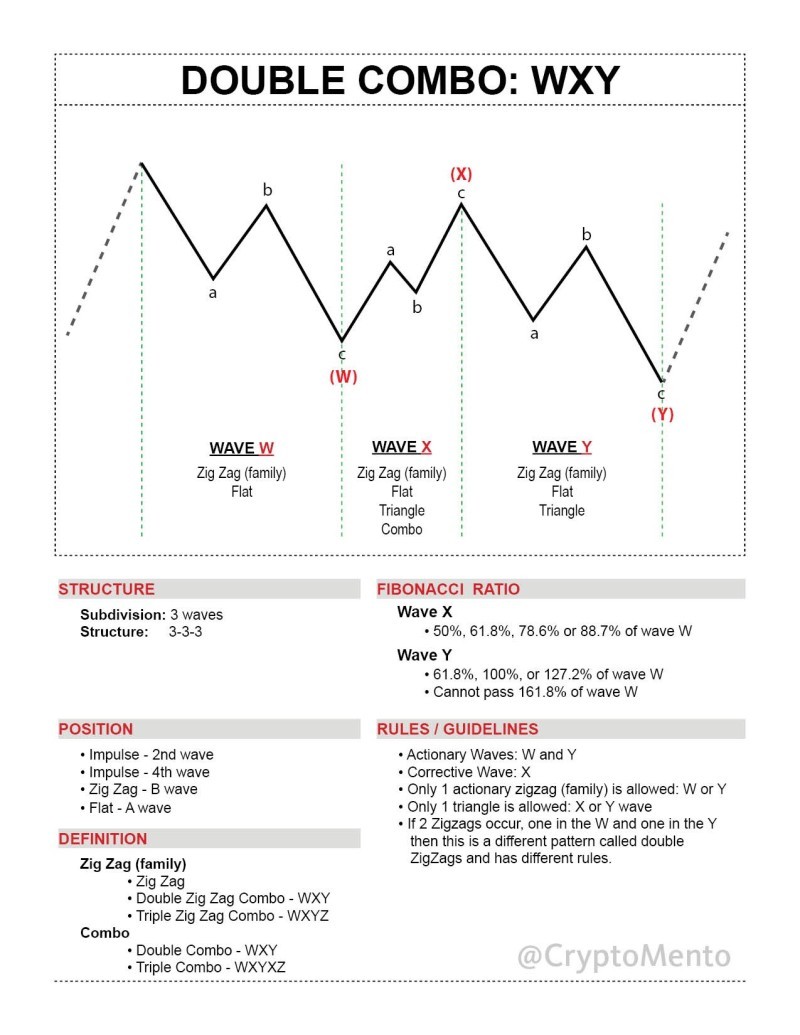
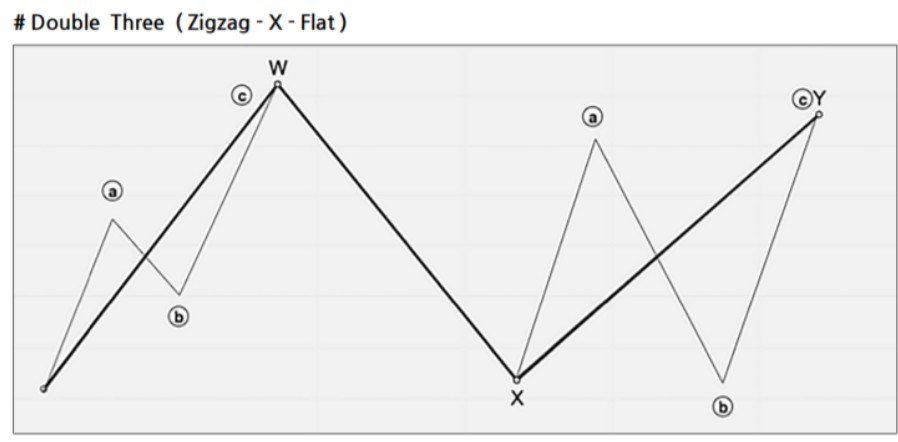
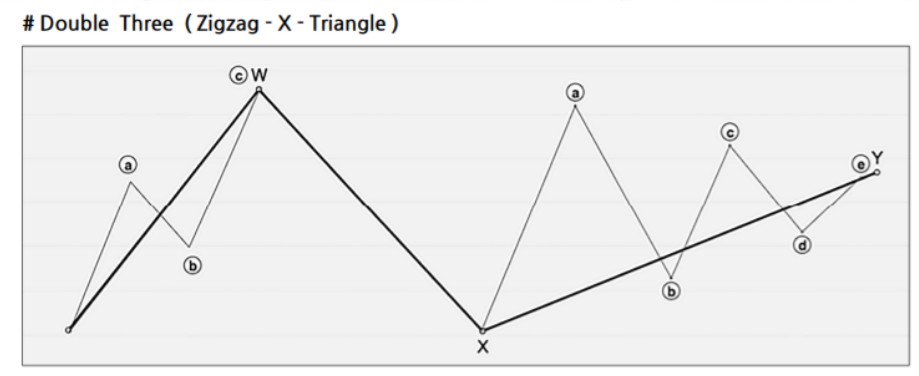
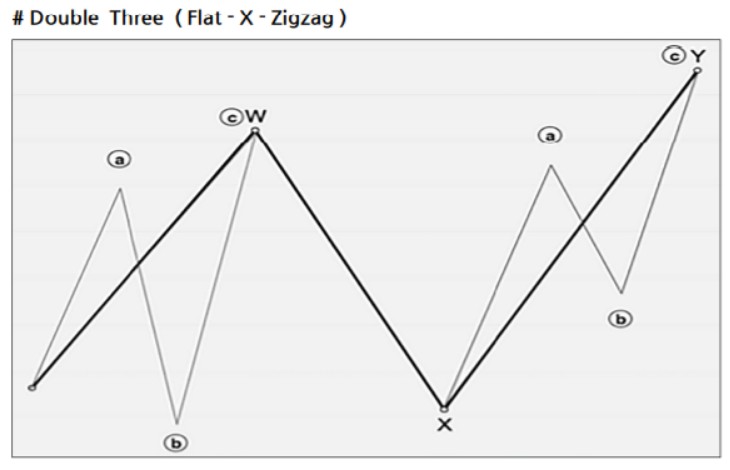
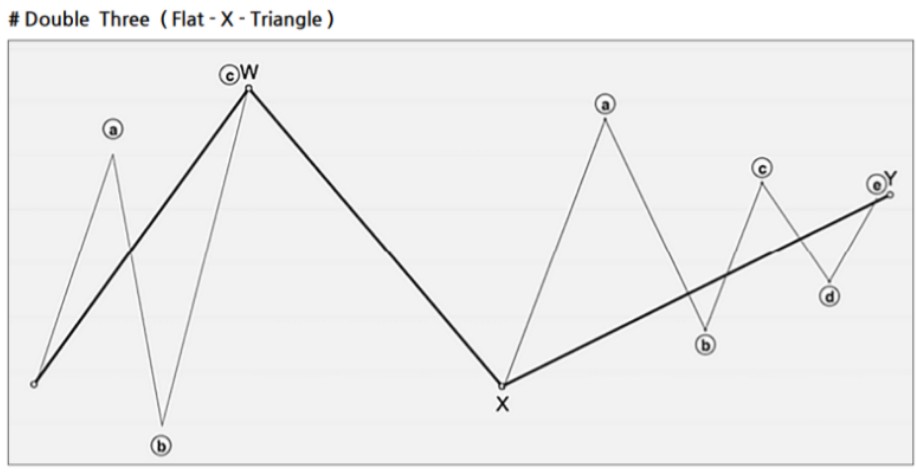
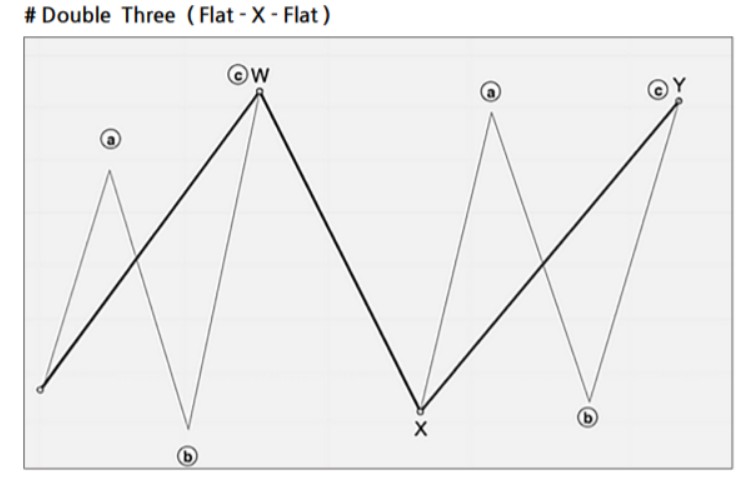
Double Combo Pattern
- Structure: W-X-Y (3 waves)
- Appearance Locations:
- In an impulse wave, during the 2nd or 4th wave
- In a zigzag correction, as the B wave
- As the A wave in a flat correction
- Wave Composition:
- W Wave: Zigzag, double zigzag, triple zigzag, or flat
- X Wave: Any form of corrective wave
- Y Wave: Zigzag, double/triple zigzag, flat, or triangle
- Fibonacci Ratios:
- X wave: 50–88.7% of the W wave
- Y wave: 61.8–127.2% of the W wave (should not exceed 161.8%)
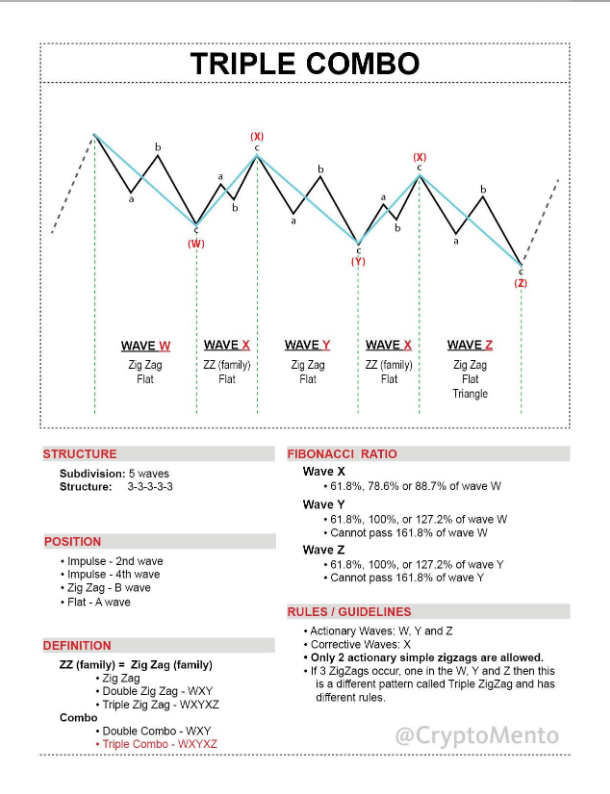
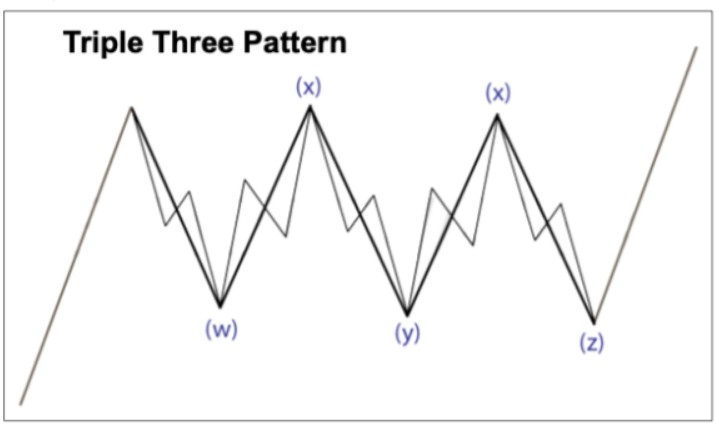
Triple Combo Pattern
- Structure: W-X-Y-X-Z (5 waves)
- Appearance Locations:
- Similarly, it can appear in the 2nd or 4th wave.
- Wave Composition:
- W Wave: Zigzag or flat
- X Wave: Zigzag, double zigzag, triple zigzag, or flat
- Y Wave: Zigzag or flat
- Next X Wave: Zigzag, double zigzag, triple zigzag, or flat
- Z Wave: Zigzag, flat, or triangle
- Fibonacci Ratios:
- X wave: 50–88.7% of the W wave
- Y wave: 61.8–127.2% of the W wave (should not exceed 161.8%)
- Z wave: 61.8–127.2% of the Y wave (should not exceed 161.8%)
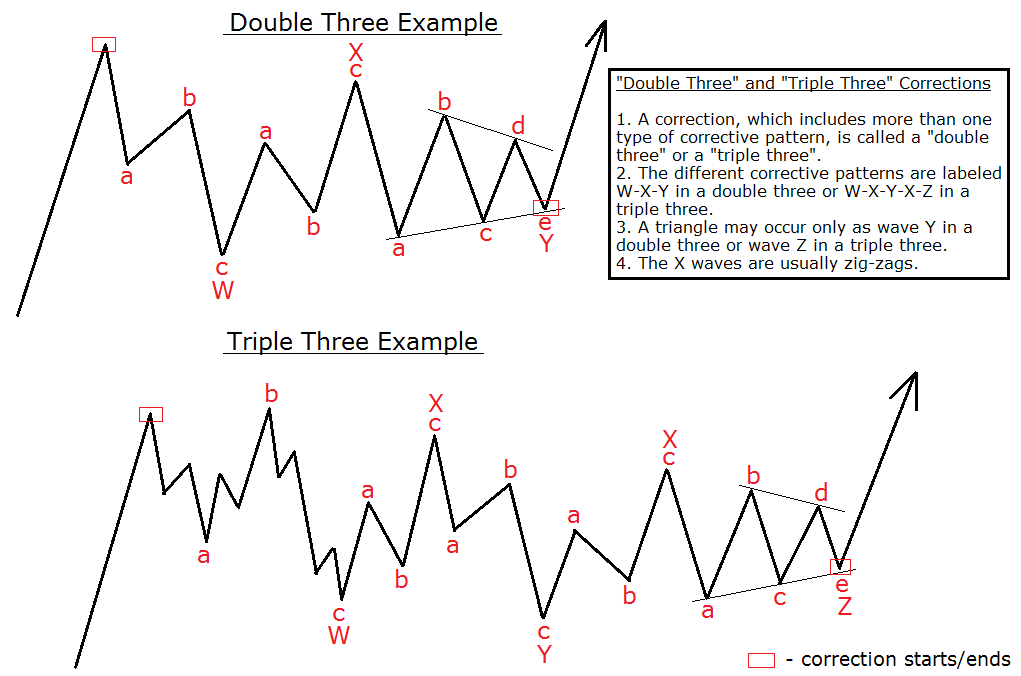
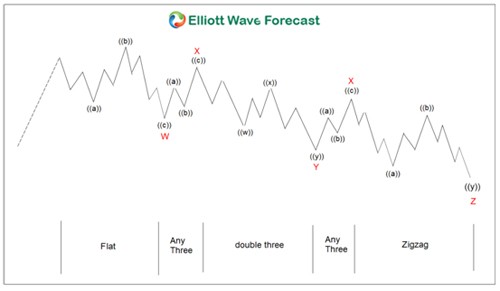
Examples of Complex Corrections
Complex corrective patterns occur when market corrections become intricate, combining various forms of corrective waves. For example, a stock might show the following pattern after a strong rally:
- Double Combo: After a strong rise, if the stock experiences a zigzag correction in the W wave, followed by a complex correction in the X wave, it might form another zigzag pattern in the Y wave.
- Triple Combo: As the market undergoes corrections, multiple zigzag and flat corrections might combine to form a pattern. For instance, the first W wave could be a zigzag, followed by a flat correction in the X wave, then the second Y wave appears as another zigzag, leading to subsequent X and Z waves.
These complex corrective patterns play a crucial role in identifying price direction. Applying various forms and Fibonacci ratios is essential for determining accurate entry and exit points.
728x90

댓글